No products in the cart.
Work From Home
7 Interesting Facts About Common Criteria
Home Business Magazine Online
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CC) is an internationally accepted and scalable set of cybersecurity certification standards (ISO 15408). Common Criteria certification ensures that the assessments of the relevant IT product were completed to consistently high criteria, in a rigorous, standardized, and repeatable manner. This article provides insight into this topic and presents 7 interesting facts about Common Criteria.
1. Internationally recognized IT security certification
Originally, Common Criteria was developed in collaboration with six countries: Germany, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Canada, and the United States. Today, Common Criteria are the driving force behind the broadest mutual acceptance of secure IT products available. It is recognized by the 31 CCRA member countries and valued by their Federal and Government entities.
2. CC evaluation process can improve the assessed IT product
The Common Criteria evaluation process enhances an IT product or system by exposing vulnerabilities that may be fixed before introducing it to the market. This also helps to avoid costly post-release updates. Furthermore, Common Criteria certification is an effective tool for keeping the business environment competitive. In order to compete with other well-established cybersecurity solutions that have previously been assessed, CC evaluation and certification are critical for the given IT product.
3. Three essential parties are involved in a Common Criteria certification process
There are three primary parties involved in the Common Criteria evaluation process:
- The Certification Body is responsible for issuing Common Criteria certifications.
- Sponsors and developers that submit their system or IT product for evaluation. In the case of large companies, this role is often the same.
- The independent and authorized laboratory that carries out the assessment.
4. A total of 7 Evaluated Assurance Levels are defined in the Common Criteria
Before starting the assessment procedure, the Sponsor or Developer has to select the Evaluated Assurance Level against which the Common Criteria evaluation will be performed.
There are 7 EAL levels defined in the Common Criteria:
- EAL1: Functionally Tested
- EAL2: Structurally Tested
- EAL3: Methodically Tested and Checked
- EAL4: Methodically Designed, Tested, and Reviewed
- EAL5: Semi-Formally Designed and Tested
- EAL6: Semi-Formally Verified Design and Tested
- EAL7: Formally Verified Design and Tested
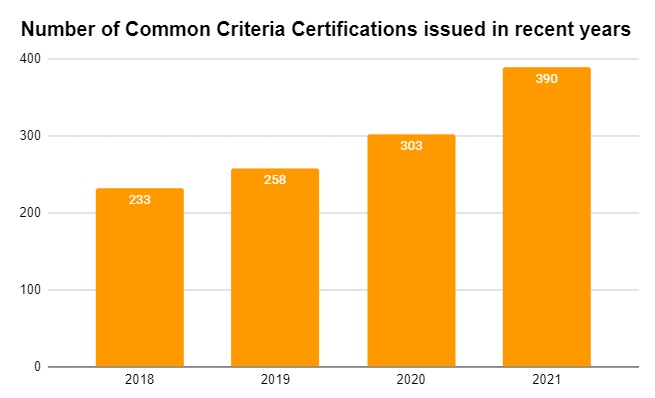
5. There is a slow but steady growth in the number of Common Criteria certifications worldwide
Since 2010, a total of 1645 IT products have been certified, with 589 of them being ICs, smart cards, smart card-related devices, and systems. Other popular product categories include Network and Network-Related Devices (237 Common Criteria certifications) and Multi-Function Devices (233 CC certifications). Aside from these, several Operating Systems, Databases, Access Control Devices, Boundary Protection Devices, and Systems passed the Common Criteria assessment process successfully.
In recent years, the number of certifications issued has increased by an average of 10%.
Data sources: https://www.commoncriteriaportal.org/products/stats/
6. New Zealand became a certificate-consuming country
After many years of the close alliance between Australia and New Zealand in managing the Australasian Certification Authority, New Zealand has opted to give up its authorizing position and remain a certificate-consuming nation in the CCRA. This is to more accurately represent New Zealand’s contribution to the Australasian Information Security Evaluation Program (AISEP) and the CCRA. The AISEP program name has been modified from ‘Australasian’ to ‘Australian’ to better represent the program’s status as a certificate authorizing nation of the CCRA. These modifications took effect in October 2021.
7. EUCC is replacing the European SOGIS mutual recognition agreement
The EUCC cybersecurity system developed by ENISA (the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity) will take the place of the existing European SOGIS mutual recognition agreement (Senior Officers Group for Information Systems). EUCC is a Common Criteria-based certification system that combines the globally acknowledged, proven methodologies of Common Criteria with new concepts to give stakeholders a contemporary and flexible solution, such as patch management for certified systems and products.
the post 7 Interesting Facts About Common Criteria appeared first on Home Business Magazine.